Flip-flops are major segments in the realm of advanced hardware. These gadgets are utilized as clock dividers and one-piece stockpiling components, and by associating numerous flip-tumbles in the correct way you can make move registers, stockpiling registers, and counters. Not at all like simple rationale doors, flip-flops use criticism to make circuits (called consecutive rationale, rather than combinational rationale) in which the future state is impacted by the past state.
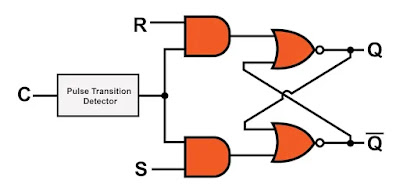
On the off chance that you need to make a flip-slump, you begin with a gated hook, for example, the gated SR lock:
A gated hook is a valuable segment, yet the yield can change at whatever point the empower flag is high. This presents an absence of accuracy and dependability into whatever advanced interface is worked around the lock. It would be better if the lock would react to include changes just at a particular minute in time. The inconvenience is, once we have actualized this usefulness, the lock is not any more a hook. It's a flip-tumble.
The beat progress finder (PTD) changes over a rising or falling edge into a short heartbeat. This heartbeat turns into the empower flag, with the end goal that the hook is empowered just for a brief timeframe following the change. The lock in addition to PTD game plan is the thing that we call a flip-flounder, and since we're typically working with rationale circuits that are administered by clock flags, the flip-tumble's empower flag is regularly alluded to as essentially the clock.
The T Flip-Slump
The basic normal for a flip-flounder is that it changes its yield state in light of a positive or negative progress on the control flag. Be that as it may, there is something else entirely to a flip-tumble than this: we likewise need to characterize the contribution to-yield relationship. This is the reason there are distinctive kinds of flip-flops; they are on the whole touchy to clock edges, however they perform diverse activities in light of the information states.
The "T" in "T flip-slump" remains for "flip." When you flip a light switch, you are changing from one state (on or off) to the next state (off or on). This is comparable to what happens when you give a rationale high contribution perfectly flip-tumble: if the yield is as of now rationale high, it changes to rationale low; if it's right now rationale low, it changes to rationale high. A rationale low information causes the T flip-slump to keep up its present yield state.
Here is a similar data in truth-table shape:
From SR or JK to T
You can change the contribution to-yield relationship of a current flip-tumble by including rationale doors and suitable interconnections. AAC as of now has a plenitude of data on this subject; on the off chance that you need to investigate the subtle elements, our article on the change of flip-flops is a decent place to begin. In this short article, I'll just present two different ways to make a T flip-flounder from a current flip-tumble.
In the event that you have a SR flip-tumble, all you require is two AND entryways to transform it into a T flip-slump:
The procedure is much less demanding in case you're beginning with a JK flip-slump. No extra entryways are required; you should simply associate a similar info flag to both information pins:







Do you know that there are readers loving to read your posts everyday? So please write and post more. I choose to follow your writing because they bring me what I want. They have knowledge and information. I will support you a lot. Thanks
ReplyDeletebest shopify apps to boost sales in 2019 || the best currency converter shopify || sale discount app on Shopify